Fundamental Research Activity:
My fundamental research activity takes place in the Adhesion and Inflammation laboratory, which applies quantitative biophysical methods to immunological questions. This laboratory brings together biophysicists, scientific immunologists, and medical immunologists. My main subject is the quantification of molecular interactions, primarily antibody-antigen and TCR-pMHC interactions, using the laminar flow chamber. These measurements allow us to quantify the kinetic properties of bonds at the level of individual bonds under realistic conditions for receptors and ligands bound to cell membranes: in these conditions, diffusion is confined, and forces are exerted on the bond.
While the study of the properties of a particular bond is of fundamental interest in biophysics, immunology requires the quantification of the properties of as broad a collection as possible of antibodies or TCRs in the form of mutants or lineages varying by one or more amino acids, coupled with cellular measurements to establish correlations. I collaborate with A. van der Merwe and O. Dushek (University of Oxford, UK) regarding the activation of T lymphocytes by the TCR, and Pierre Milpied (CIML, Marseille) regarding the affinity maturation of antibodies. Two main questions are addressed: what properties of antigen-antibody and TCR-pMHC bonds are detected by cells and trigger a response? What are the relationships between sequence, structure, and functional properties of these molecules? I have therefore automated the execution and analysis of flow chamber experiments, enabling the measurement of collections of dozens of molecules, and created derivative methods to measure other parameters such as binding energy. These developments have allowed the measurement of the largest collections of TCR-pMHC and antigen-antibody interactions under force published to date and have been the subject of a series of publications on antigen-antibody bonds (Biophysical Journal 2008, 2009, 2011, 2019; Frontiers Immunology 2013, Scientific Reports 2016) and TCR-pMHC bonds (Biophysical Journal 2012, PNAS 2019, Cells 2021, EMBO Journal 2023).
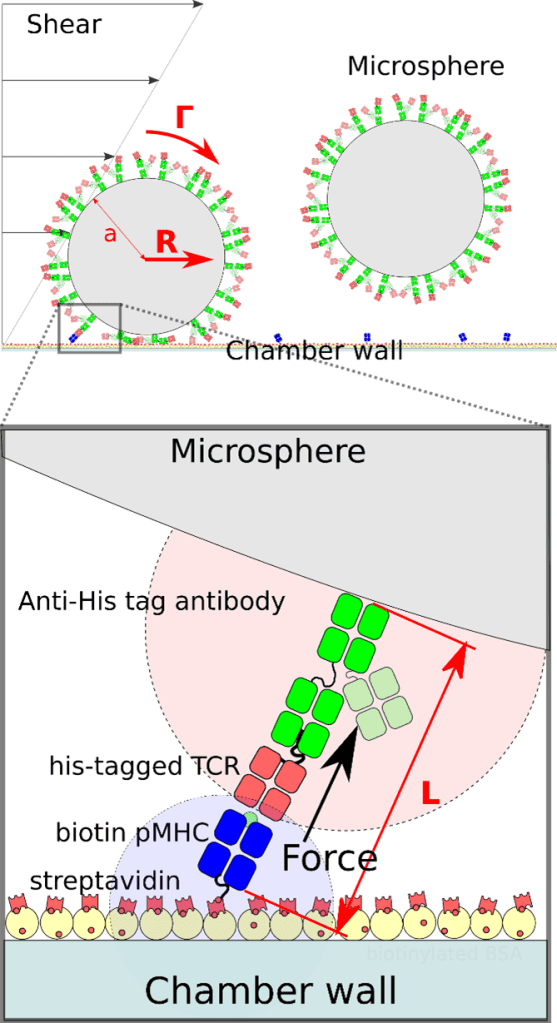
Figure 1 Top, schematic representation of two microspheres in a laminar flow chamber. The microspheres are coverdred with anti his-tag antibodies that themselves bind His-tagged TCR. Biotinylated pMHC are bound to streptavidin on the chamber bottom. Bottom is a closer representation of a microsphere-bound TCR binding a surface-bound pMHC. Force L exerted by the flow on rthe bond is a combination of torque Γ and hydrodynamic drag R.
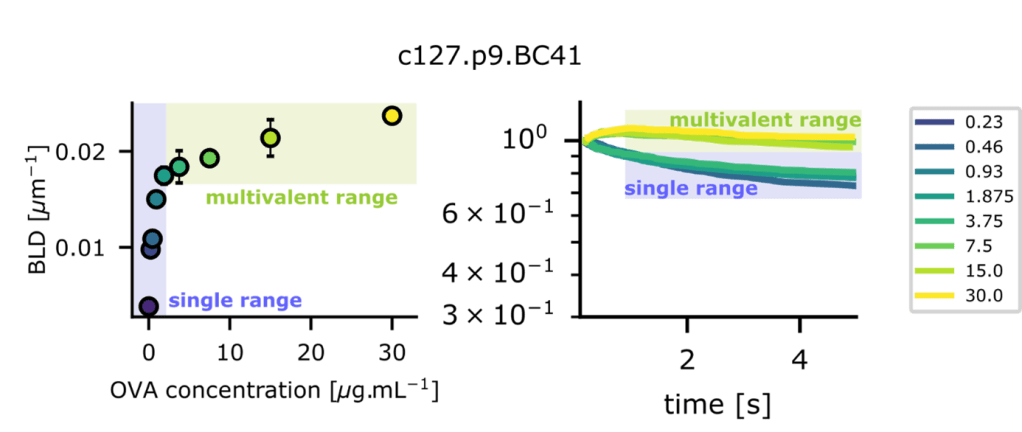
Figure 2 Demonstration of single molecular bond observation with the laminar flow chamber. Left, Binding Linear Density (or number of arrests occuring per distzance travelled by microspheres) increases proportionnally to ligand (Ova) concentration deposited in the single molecular range (0.23 µg/ml to 1.875 µg/ml). Right, in the same range, bonds lifetimes do not change as survival fractions plotted versus time superimpose for the same range of deposited molecules

Figure 3 Off-rates measured at single molecular level using our laminar flow chamber apparatus for three different antibody lineages after mouse immunization with ovalbumin (c179 in pink, c127 in grey and c87 in yellow), under five different forces. Sequences of B lymphocytes were gathered by Pierre Milpied team in CIML, allowing to identify sequences belonging to common lineages, and to determine the sequence of the germine antibody for each lineage. Antibodies were then produced in yeast. For each lineage, germline antibody is the leftmost of each color group, matured antibodies are on the right of it. Affinity maturation shows a constant gain in force resistance, measured as a diminution of off-rate between germline antibody and matured antibodies of same lineage. Moreover, off-rates are homogenous amond maturated antibodies of diffrent lineages. Germline antibodies are very sensitive to force, and have no measurable binding above 10pN.
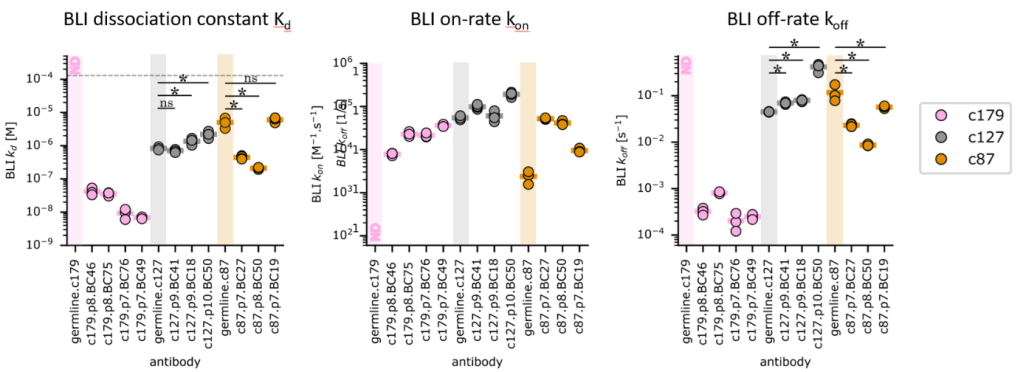
Figure 4 KD, On-rates and Off-rates measured in solution using BioLayer Inteference apparatus for three different antibody lineages after mouse immunization with ovalbumin (c179 in pink, c127 in grey and c87 in yellow. Sequences of B lymphocytes were gathered by Pierre Milpied team in CIML, allowing to identify sequences belonging to common lineages, and to determine the sequence of the germine antibody for each lineage. Antibodies were then produced in yeast. By contrast with experiments under force, antibody maturation may result in either gain or loss of affinity, while values are very heterogenous between lineages.
Medical Research Activity:
My medical research activity primarily involves quantifying the initial adhesion steps of leukocytes to the endothelium using the laminar flow chamber. This activity directly benefits from the developments made for fundamental research, particularly in data analysis. Olivier Théodoly and Marie-Pierre Valignat, biophysicists in the laboratory, are also specialists in quantifying cell migration and transmigration. We have therefore combined these methods into a common setup that allows us to quantify the essential steps of leukocyte recruitment to the endothelium (rolling, firm adhesion, migration, transmigration). This quantification of leukocyte adhesion and recruitment has been applied to the diagnosis of rare immune deficiencies (collaboration with G. Michel and P. Morange, Journal of Immunology 2011), the study of the pathophysiology of ARDS (collaboration with the intensive care unit of L. Papazian, Critical Care 2016), leishmaniasis infection (collaboration with the Dos-Santos team, Brazil, Scientific Reports 2015), and most recently, thrombosis (collaborations with P. Morange, Blood 2021, and G. Kaplanski, Haematologica 2022).
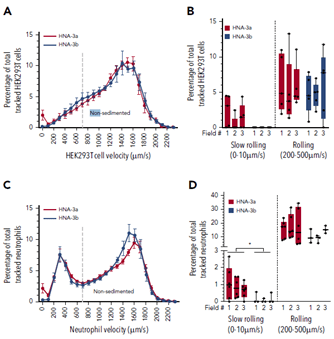
Figure 5 Top, velocities of HEK293 cells transfected with either HNA3A (red) or HNA3B (blue) when in a physiological shear flow above Willebrand factor. Histograms show the proportions of slow and fast rolling cells, with a loss of slow rolling for HNA3B cells. Bottom, velocities of patients neutrophils with either HNA3A/3A phenotype (red) or HNA3B/3B (blue) when in a physiological shear flow above Willebrand factor. Histograms show the proportions of slow and fast rolling cells, with again a loss of slow rolling for HNA3B cells.
Secondly, Olivier Théodoly and I are developing a family of methods to quantify leukocyte functions based on the micro-printing of substrates that do not require manipulation to perform the functions of sorting, stimulating, and revealing the signal of the tested cells, so that they can be widely used in hospitals with minimal labor. A patent was filed in 2021, the project received two successive PhD funding grants from the PACA-Sud region and won the 2021 AORC call for proposals from the AP-HM (innovation category), a CNRS pre-maturation contract that funded the patent, and a postdoctoral contract in 2022. The prototype allows the quantification of T lymphocyte activation. A prototype quantfying CAR-T activation is being developed in collaboration with Pr. Chabannon (Institut Paoli Calmettes, Marseille), as well as an ADCC test in collaboration with P. Rihet (TAGC, Marseille). We are currently seeking to detect the expression of soluble molecules in response to cellular activation.
In the hospital allergy sector, I am setting up the capacity to develop specific IgE assays by ad hoc ELISA, as well as punctual tests for basophil activation (an ELISpot for sensitization to donkey milk has just been successful). In response to an expressed need for the diagnosis of delayed hypersensitivity, I am developing the exploration of T lymphocytes. A master’s thesis has begun to explore sensitization to iodinated contrast products by ELISpot (a literature review is in preparation); a second thesis has begun aiming to employ our micro-printed test technology in the same context.

You must be logged in to post a comment.