Collaboration: JPK Instruments / Bruker
We use and develop Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) methods in biology.
- In imaging mode, the AFM cantilever acts as a finger to delicately delineate the topology of the surface of a sample, at nm resolution in the 3 directions of space, under physiological conditions.We use it to obtain high resolution images of proteins at work and of cells adhered to smart substrates.
- In force mode, the cantilever deflection allows the measure of the forces that are exerted on its extremity, as low as <10 pN, making the AFM a very well suited techniques for measuring the molecular interactions at the single molecule scale, in particular in the case of a ligand/receptor interaction, in Single Molecule Force Spectroscopy mode. It can also be extended to the use with living cells, in Single Cell Force Spectroscopy mode.
In LAI, we possess the expertise in “classical” Bio-AFM.
Imaging cells
We use AFM to image living or fixed cells, and couple AFM imaging to other resolutive imaging techniques such as RICM, TIRF,…
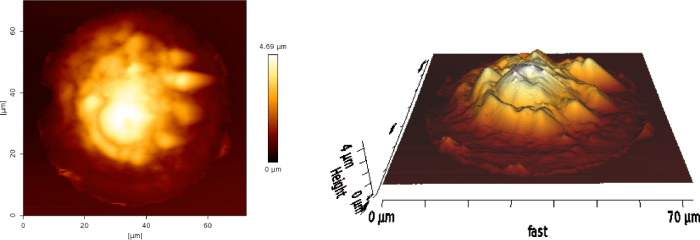
Fig: AFM contact mode image of a COS7 cell adhering on a FN pattern
Dejardin MJ, Hammerle A, Sadoun A, Hamon Y, Puech PH, Sengupta K*, Limozin L* Lamellipod reconstruction by three dimensional reflection interference contrast nanoscopy (3D-RICN). Nanoletters (2018) Oct 10;18(10):6544-6550
Coupling AFM force mode and simultaneous fluorescence imaging
We developped and easy and cheap coupling between AFM and fluorescence to allow the measurements of stimulation and activation of T cells, montitoring Ca2+ in real time, using an original internal timer signal, and AFM based mechanical stimulation.
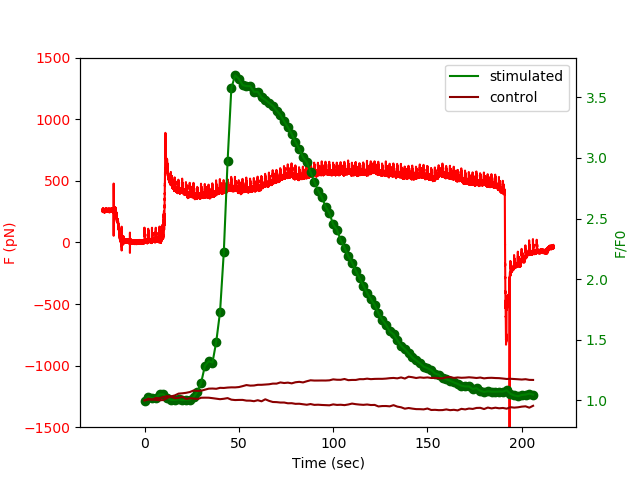
Fig: Simultaneous recording of forces (red) and calcium fluxes (green) as a function of time for a Fluo4 loaded Jurkat T cell. Fluorescence of non contacted cells in brown.
Stimulation can be performed with continusous contact or successions of timed, short stimulations in order to dissect how the “signalling black box” answers to the same specific signal, but with a given spatial or temporal distribution. This approach, in a way, is a typical physicist method of dissecting the “transfer function” of an unknown system. We extended this technique to study of modifications of mechanical properties of T cells by using photoactivable small GTP-ases family members (eg. Rac-PA) in real time.
Synchronizing atomic force microscopy force mode and fluorescence microscopy in real time for immune cell stimulation and activation studies. Cazaux S, Sadoun A, Biarnes-Pelicot M, Martinez M, Obeid S, Bongrand P, Limozin L, Puech PH*. Ultramicroscopy. 2016 Jan;160:168-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ultramic.2015.10.014. Epub 2015 Oct 19
Mechanical characterization of cells
We apply AFM indentation to characterize cell mechanics, in pathological or normal situations, using home made modified cantilevers, eg. by glueing beads of desired diameter and chemistry to the end of commercial levers. For that, we use micromanipulations techniques (see dedicated page).
We use patterned cells to reduce the variability and increase the statistics of single cell mechanical AFM measurements.
We also compare our AFM mechanical data with other techniques available in the lab (MP, optical tweezers) or through collaborations.
Controlling T cells spreading, mechanics and activation by micropatterning. A. Sadoun, M. Biarnes-Pelicot, L. Ghesquiere-Dierickx, A. Wu, O. Théodoly, L. Limozin, Y. Hamon, P.-H. Puech, Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 24;11(1):6783. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86133-1
Single-cell immuno-mechanics: rapid viscoelastic changes are a hall-mark of early leukocyte activation Alexandra Zak, Sara Violeta Merino Cortés, Anaïs Sadoun, Farah Mustapha, Avin Babataheri, Stéphanie Dogniaux, Sophie Dupré-Crochet, Elodie Hudik, Hai-Tao He, Abdul I Barakat, Yolanda R Carrasco, Yannick Hamon, Pierre-Henri Puech, Claire Hivroz, Oliver Nüsse, Julien Husson, Biophys J. 2021 May 4;120(9):1692-1704. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2021.02.042
iASPP contributes to cortex tension, astral microtubule capture and mitotic spindle positioning via EB1 and Myo1. Aurélie Mangon, Danièle Salaün, Mohamed Lala Bouali, Sabine Quitard, Daniel Isnardon, Stéphane Audebert, Pierre-Henri-Puech, Pascal Verdier-Pinard et Ali Badache, J Cell Biol. 2021 Dec 6;220(12):e202012002. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202012002

You must be logged in to post a comment.